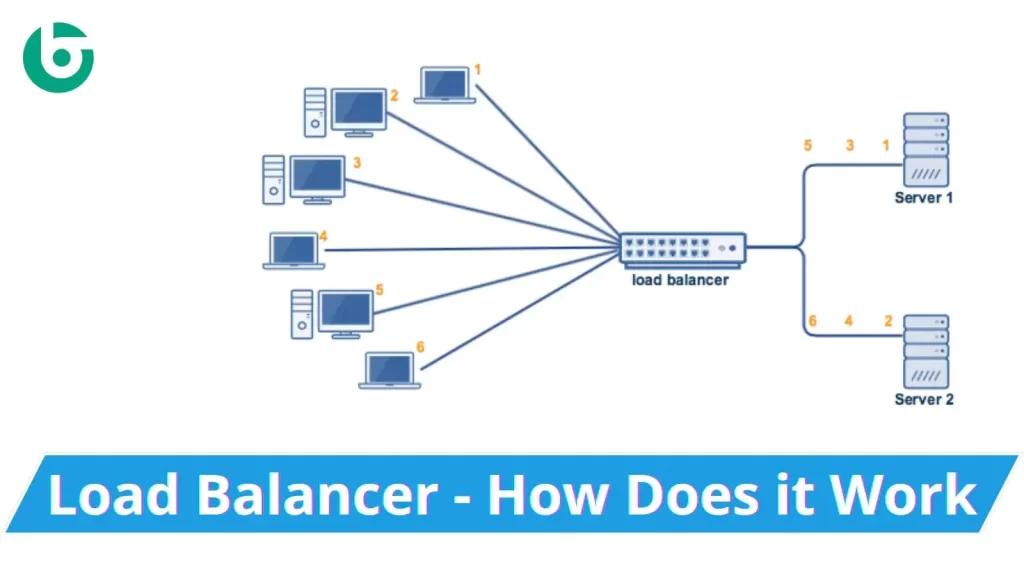
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses rely on complex IT infrastructures to support their operations, deliver services, and meet customer expectations. A critical component of this infrastructure is the load balancer. As enterprises increasingly depend on cloud-based services, distributed systems, and microservices, the role of load balancers in IT has never been more vital. In this blog, we’ll explore what load balancers are, their importance in modern IT environments, the benefits they provide, and why they are indispensable in ensuring seamless, efficient, and reliable service delivery.
What are Load Balancers?
Load balancers are specialized devices or software that distribute network or application traffic across multiple servers or resources. The primary function of a load balancer is to ensure that no single server bears too much demand by evenly distributing incoming requests. This balancing act optimizes resource use, improves response times, and prevents any one server from becoming a point of failure, thereby increasing the availability and reliability of applications.
There are two main types of load balancers:
Hardware Load Balancers
These are physical devices installed within an organization’s IT infrastructure. They are known for their high performance, stability, and ability to handle large volumes of traffic. However, they can be costly and less flexible than their software counterparts.
Software Load Balancers
These are software applications that run on standard servers, offering more flexibility and scalability than hardware load balancers. They are typically more cost-effective and are commonly used in cloud environments or with virtualized resources.
Load balancers can operate at different levels of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, primarily at Layer 4 (Transport Layer) or Layer 7 (Application Layer):
Layer 4 Load Balancers: These manage traffic based on network and transport protocols (e.g., IP, TCP, UDP) without considering the content of the traffic.
Layer 7 Load Balancers: These are more sophisticated, as they operate at the application layer, making routing decisions based on the content of the request (e.g., HTTP headers, cookies). They are ideal for managing web traffic and delivering applications more efficiently.
Read More : Revolutionizing IT with Microservices Architecture
Importance of Load Balancers in IT
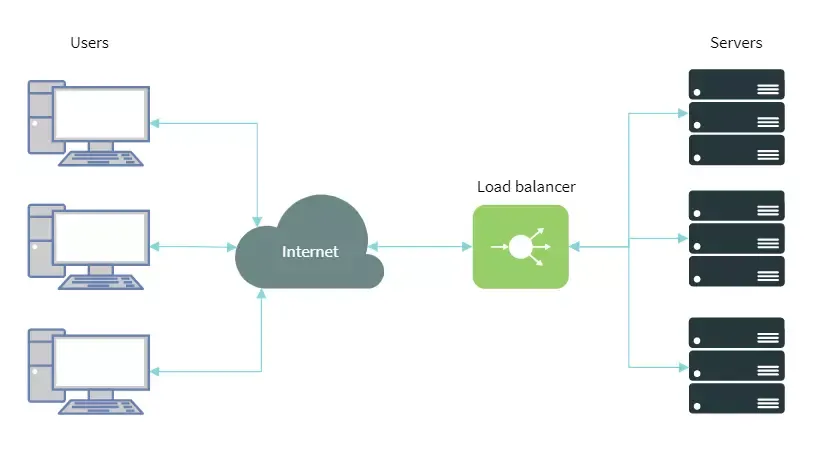
As organizations adopt more complex IT infrastructures, load balancers play an increasingly critical role in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of their systems. Here’s why load balancers are so important in modern IT:
Ensuring High Availability
One of the primary reasons for using load balancers in IT is to ensure high availability. By distributing traffic across multiple servers, load balancers reduce the risk of a single point of failure. If one server fails, the load balancer automatically redirects traffic to other functioning servers, ensuring that services remain available to users.
Optimizing Performance
Load balancers help optimize the performance of applications by distributing traffic in a way that maximizes the use of available resources. By ensuring that no single server is overloaded, load balancers prevent bottlenecks, reduce latency, and improve the overall user experience.
Scalability
As businesses grow, so do their IT demands. Load balancers allow organizations to scale their infrastructure efficiently by adding or removing servers as needed without disrupting service. This scalability is essential for businesses that experience fluctuating traffic or seasonal spikes in demand.
Security Enhancement
Load balancers contribute to the security of IT environments by masking the IP addresses of backend servers and providing a first line of defense against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Some advanced load balancers also include features like SSL termination, which offloads the decryption work from servers, further enhancing security and performance.
Efficient Resource Utilization
In environments where resources are shared across multiple applications, load balancers ensure that these resources are used efficiently. They can allocate resources based on demand, ensuring that applications receive the necessary processing power, memory, and bandwidth when they need it.
Read More : All You Need To Know About Full Stack Web Development
Benefits of Load Balancers in IT
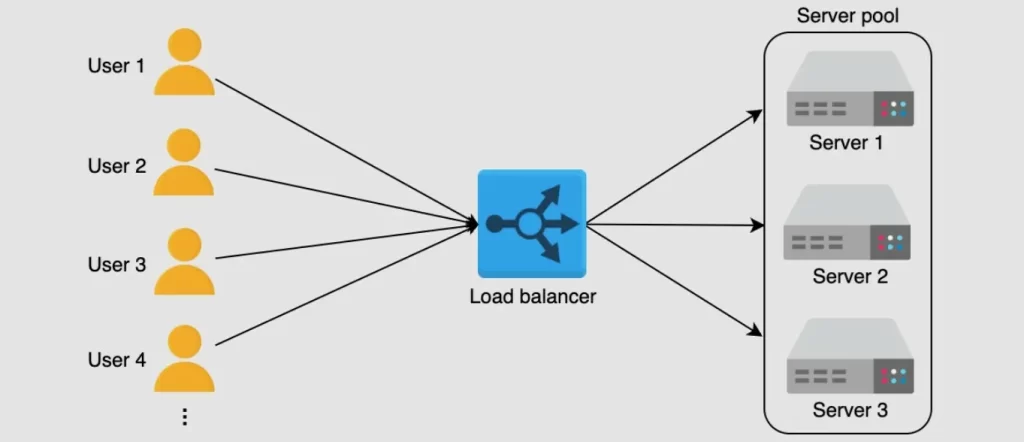
Load balancers provide numerous benefits that extend beyond just balancing traffic. Here are some of the key advantages:
Improved Redundancy and Fault Tolerance
By distributing traffic across multiple servers, load balancers enhance redundancy and fault tolerance. If one server fails or needs maintenance, others can pick up the load, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuity of service.
Better User Experience
Load balancers play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth user experience. By distributing traffic efficiently, they reduce response times and prevent service disruptions, leading to a more responsive and reliable application performance.
Cost Savings
While there is an initial investment in deploying load balancers, they can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. By optimizing resource use and preventing downtime, load balancers reduce the need for additional hardware and minimize the costs associated with service outages.
Flexibility in Deployment
Modern load balancers offer great flexibility in deployment, allowing organizations to choose between on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid models. This flexibility ensures that load balancers can be tailored to meet the specific needs of any IT environment.
Enhanced Security Posture
Beyond just traffic distribution, load balancers can act as a security layer, protecting backend servers from direct exposure to external threats. Features like web application firewalls (WAF), SSL termination, and DDoS protection further strengthen an organization’s security posture.
Simplified Management and Maintenance
Load balancers simplify the management and maintenance of IT infrastructure. They allow for easier scaling, streamlined updates, and the ability to perform maintenance on servers without affecting end-user experience. This centralized management reduces complexity and helps IT teams maintain a robust and efficient environment.
Conclusion
In the modern IT landscape, where reliability, performance, and security are paramount, load balancers are indispensable. They ensure that applications remain available and responsive even during peak demand, prevent bottlenecks, and enhance security. As organizations continue to embrace cloud computing, microservices, and distributed systems, the role of load balancers in IT will only become more critical. Whether deployed on-premises or in the cloud, load balancers provide the foundation for scalable, resilient, and efficient IT infrastructure, making them a cornerstone of any robust digital strategy.
